Putting The “YOU” in U-Factor
When shopping for new windows, one of the most important technical specifications to consider is the U-factor. This value directly influences a window’s energy efficiency, comfort level, and overall performance in your home. But what exactly does is this measurement, and why is it essential for homeowners to keep it in mind? This article will break down the U-factor, its significance, and how it can impact your home’s energy usage and your wallet.

What is the U-Factor?
Also known as thermal transmittance, the U-Factor measures the rate at which heat flows through a window. Essentially, it indicates how well a window insulates against the cold in winter or the heat in summer. The lower the number, the better the window is at insulating your home. In other words, a lower U-factor means less heat escapes your home, resulting in better energy efficiency and a more comfortable indoor environment.
U-factor is expressed in terms of BTU (British Thermal Units) per hour, per square foot of window area, per degree Fahrenheit of temperature difference between the indoor and outdoor environments. Typical U-factor values for windows range from 0.20 to 1.20, with values lower than 1.0 generally considered better for insulation.
U-Factor vs. R-Value: What’s the Difference?
While both U-factor and R-value pertain to the insulation properties of windows (and other building materials), they measure slightly different things. The U-factor measures how much heat is lost or gained through a material, with lower values representing better insulating performance. The R-value, on the other hand, measures the material’s ability to resist heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the material is at resisting heat transfer.
When considering windows, a lower U-factor indicates better energy performance, while a higher R-value suggests better thermal resistance. However, for windows, the U-factor is the key figure to focus on since it directly correlates to how well a window performs in keeping your home’s temperature regulated.
A good trick to remember the difference is that the U-Factor is inverse to the R-Value. For example, if you have a U-Factor of .20, then the R-Value is 5 Or “1÷.20=5”.
How This Impacts YOU
For homeowners, understanding the U-factor is vital for several reasons. Let’s explore the primary benefits of choosing windows with a low U-factor:
1. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
The most significant benefit of selecting windows with a low U-factor is the potential for energy savings. Windows are one of the main points where heat is lost in a home. Whether it’s the middle of winter or the peak of summer, inefficient windows can cause your heating or cooling system to work harder to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. This leads to higher energy consumption and increased utility bills.
By choosing windows with a low U-factor, you can reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. This means your home will maintain a more stable temperature, and your HVAC system won’t have to work overtime. Over time, these energy savings can add up to significant cost reductions, making it a smart investment for homeowners looking to lower their monthly energy bills.
2. Comfortable Living Environment
A window’s U-factor not only affects energy efficiency but also contributes to the comfort level inside your home. Poorly insulated windows can cause noticeable temperature fluctuations in the rooms near them. Drafts may occur in the winter, and you might feel uncomfortably warm near the windows during the summer months.
Windows with a low U-factor provide better insulation, leading to a more consistent indoor temperature. With less heat transferring through the glass, you’re less likely to experience cold spots in the winter or heat buildup during the summer. This results in a more comfortable living environment, which is one of the main reasons homeowners choose to upgrade their windows.
3. Improved Indoor Air Quality
In addition to keeping temperatures stable, energy-efficient windows can also improve your home’s indoor air quality. When windows have a high U-factor and allow excessive heat loss or gain, your HVAC system has to work harder to regulate the indoor environment. This can lead to air imbalances, especially if the system is older or not well-maintained. By choosing windows with a low U-factor, you can reduce the strain on your HVAC system, promoting better air circulation and more even temperature distribution throughout the house. This can have a positive impact on both comfort and air quality.
4. Environmental Impact
Homeowners who are environmentally conscious will appreciate the role that low U-factor windows play in reducing a home’s carbon footprint. Since these windows are more energy-efficient, they reduce the amount of energy required to heat or cool your home. As a result, less energy is consumed, leading to fewer greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. By making the switch to energy-efficient windows, homeowners contribute to environmental sustainability while also benefiting from long-term cost savings.
5. Potential for Rebates and Tax Incentives
Many homeowners are unaware that energy-efficient windows may qualify for rebates or tax incentives. Governments at the federal, state, and local levels often offer financial incentives to encourage the adoption of energy-efficient home upgrades. By choosing windows with a low U-factor, you may be eligible for tax credits, rebates, or other incentives that can reduce the upfront cost of purchasing and installing new windows. You can learn more about tax rebates offered here.
Before purchasing, check with local authorities or consult the manufacturer to see if any incentives are available for the windows you’re considering. This can help offset the initial investment and further enhance the overall cost savings.
Factors That Influence U-Factor
It’s important to note that the U-factor of a window can be influenced by several factors, including the materials used, the type of glazing, and the presence of gas fills. Here are some key impactful elements:
1. Frame Material
The material of the window frame plays a significant role in the U-factor. Frames made from materials like wood, vinyl, or fiberglass typically have lower U-factors compared to metal frames. Metal frames tend to conduct heat more easily, making them less energy-efficient. For the best performance, homeowners often choose windows with non-metal frames or frames that incorporate a thermal break (a layer of insulating material that separates the inside and outside of the frame). Keep in mind hollow chambers don’t perform as well as foam filled chambers. Within the fenestration industry, extruded polystyrene and expanding polyurethane are used to fill these cavities. Of the two, expanding polyurethane provides better insulation (by between 7-15%) due to its ability to fill the entire chamber while extruded polystyrene fits into the pocket loosely.
2. Glazing Type
The type of glazing (or glass) used in a window also affects the U-factor. Single-pane windows have the highest U-factors, as they offer minimal insulation. Double- or triple-glazed windows are much more energy-efficient, especially if they are filled with insulating gases. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings, which reflect the ideal indoor temperature back into the room, while blocking undesirable outdoor temperatures from entering the home. This can also reduce the U-factor by 35-55% compared to using an uncoated pane depending on which glass type is used.
3. Gas Fill
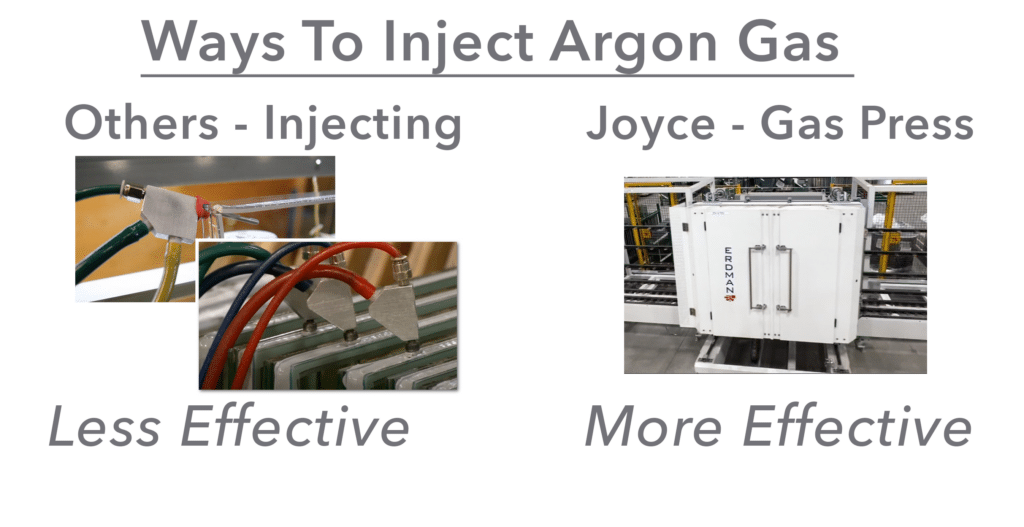
Windows provide the best energy efficiency when insulating gas is present between the panes. Some windows are filled with an insulating gas, like argon or krypton, between the panes of glass. These gases have a lower thermal conductivity than air, helping to further reduce heat transfer and improve a window’s U-factor. Windows without gas fills typically have a higher U-factor, making them less efficient. Here at Joyce, we ensure our windows are filled with at least 90% argon gas to provide top notch insulation for decades.
When shopping for new windows, the U-factor is an essential value to consider. A lower U-factor means better energy efficiency, lower heating and cooling costs, and a more comfortable indoor environment. Homeowners who choose windows with a low U-factor will see long-term benefits in terms of cost savings, comfort, and environmental impact. Be sure to evaluate the U-factor of any window you are considering to make an informed decision that will provide lasting benefits to your home.